Although you may know how to search for the best keywords you may not be aware of the technical issues of SEO such as reviewing your sitemap or making it more crawlable. Remember, it’s always the technical aspects that determine whether you succeed or not. It’s, therefore, important to ensure that all your technical issues are found and sorted out before creating and optimizing your content. Regardless of how intimidating your technical SEO may seem, you should know about it.
Technical SEO Practices to Ensure Your SEO is Solid
1. Protect your site from negative SEO
Sometimes your competitors may play dirty and do everything that they can to outrank you. Although your site may not be attacked, it’s important to always be prepared so as to prevent this. Negative SEO not only results in reduced organic search visibility but also lost sales and revenue.
To save your site from this, you need a regular backlink monitoring. If you suddenly see a huge drop or spike in the number of inbound links and you have not been doing anything then you need to investigate what could be wrong.
With the help of some tools, you can check how many backlinks your site has received. Take a look at WooRank’s SEO Review where you can check your site backlink counter side by side with your top 3 competitors:
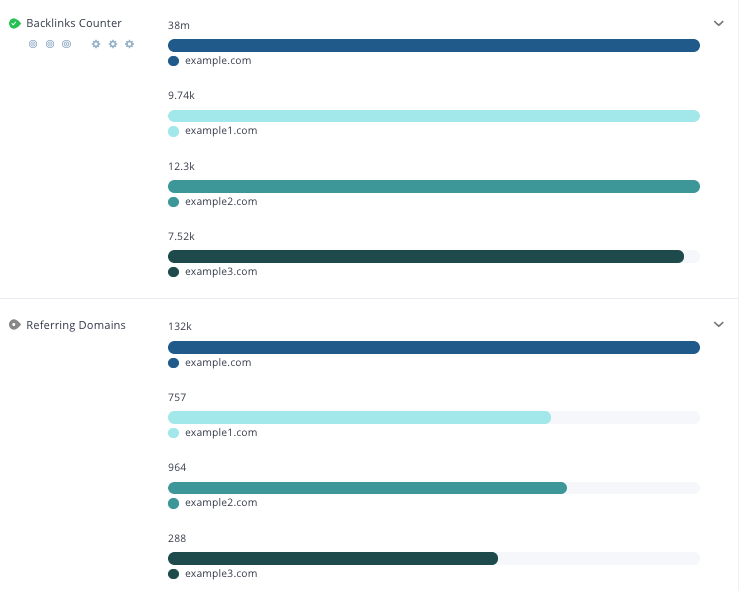
To be sure that you are not missing on any negative SEO, it’s important to check your backlinks every week.
2. Check for unindexable content types
Before indexing your web pages, they have to be crawled. By using some tools like our Site Crawl, you can check if your website can be crawled by Google. You may also use this tool to prevent some the indexing of some pages (example: if tags or categories create duplicate content)
There are certain types of content, such as Flash and frames, that they can’t properly crawl or index. If you want to add effects, you’re better off using HTML5, JavaScript or CSS, which Google is able to properly load. It’s important for search engines to view the pages like they are supposed to be so as to gauge their quality and content.
If your website is not crawlable then Google won’t index it.
3. Optimize your crawl budget
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages on a single domain that search engines can crawl within a given period of time. Check out Google’s explanation of crawl budget here.
Once you are aware of crawl budget, you must optimize your website to make the most of it. Although most people do not know how Google assigns crawl budget to websites, there are two theories that can explain this. First, it’s the number of internal links and second, the number of links from other sites.
Although you can’t grow your backlinks immediately, here are two major ways to optimize your crawl budget
Remove duplicate pages
Every duplicate page crawled is a waste of Google’s crawl budget so. You don’t have to delete duplicate pages, but you can "hide" them from Google. Use canonical tags, NoIndex tags to point crawlers away from duplicate pages.
Prevent indexation of pages that do not have any SEO value.
Terms and conditions, privacy policies, expired promotions, tag and category pages are some of the things that you need to consider. These pages likely won’t help you achieve your business goals so there’s not much point in have Google waste time crawling them.
You should also define certain parameters so that Google doesn’t end up crawling the same pages.
4. Improve your on-page speed
Loading time has a great impact on a page’s SEO. You, therefore, need to check your site’s load time and speed and find the issues slowing it down.
If your site’s speed is much less than the way it’s supposed to be you can greatly boost it by resizing graphics and your images, linking to external pages or preloading your content.
Remember, page speed is not only important for your visitors but for the search engines as well. Most visitors who are impatient don’t like waiting for the site to load and Google doesn’t want to recommend those slow pages to its users. The speed test will, therefore, detect some of the issues that might prevent your page from loading fast.
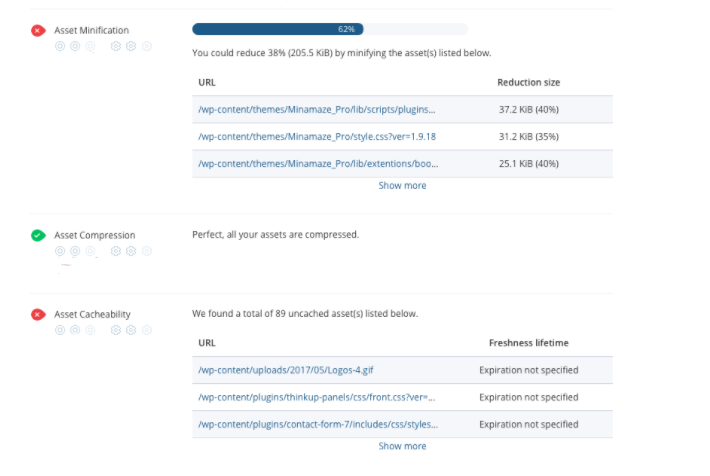
Our WooRank Review goes deeper than page speed or load time, providing exactly what file caused your pages to be too slow. If you click on show more to find exactly what the issue is and fix them to increase your load time.
Learn more about how to optimize your page load time.
5. Remove any broken links
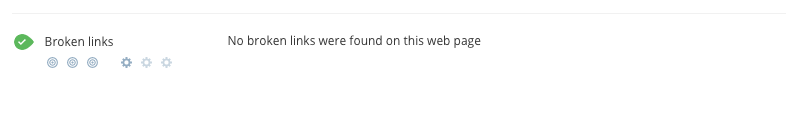
Broken links are both harmful for your site's SEO and bad for user experience. Dead links directly prevent search engines from crawling your site because they use links to get from page to page. A broken internal link on your site is like a bridge being out on the highway.
Since Google would want to send its searches to high-quality sites hence broken links are obviously a red flag to this. Ensure that you detect and rectify any broken links that you may be having on your website. You can always use tools such as WooRank to check if at all your site may be having any anchors or broken links.
6. Make your site mobile friendly
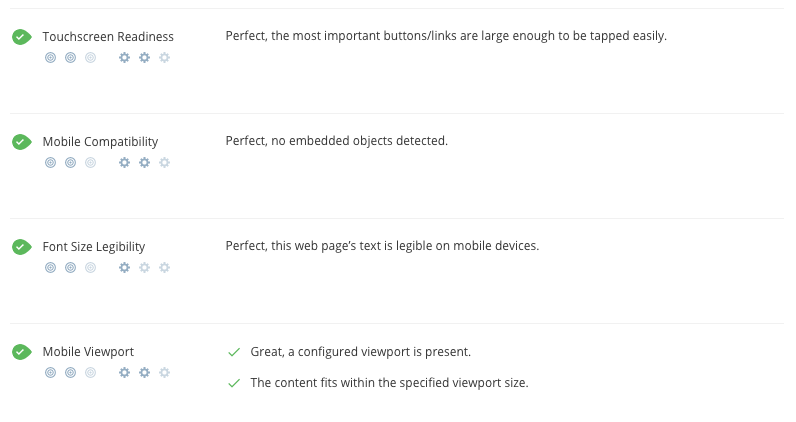
If your website is mobile friendly, it will have a huge impact on its current ranking and even bigger impact in the future. With Google’s mobile friendliness test, you can check if your blog or website site optimized for the mobile user experience.
Boosting your mobile performance depends on factors such as the article lengths, fonts, viewport, content compatibility, types of headlines or the format of the articles.
7. Review your sitemap
Wait! Let’s go back to sitemaps.
If you’re using a CMS to build out your site or designing a fully coded site, the sitemap is one of the most neglected tasks. Take a closer look at how your sitemap is working, especially in regards to WordPress where everything is plug and play.
Sitemaps tell search engines where to find all of your content, and how often those pages are updated so they can be able to locate any new content faster.
Here are some things you should check your sitemap for:
- Freshness: Whenever new content has been updated, your XML map should be updated. Your CMS should do this automatically, but it’s best to check manually.
- Cleanliness: You need to ensure that your sitemap is free from garbage such as relative links and non-canonical URLs. You also need to regularly check your sitemap for any syntax errors that might occur.
- Size: Although Google limits the number crawls to 50,000 URLs, keep them much shorter than that. By reducing the number of URLs you will be able to yield more effective crawls.
Check out our Guide to XML Sitemaps
Now Dig Deeper
You can check individual pages manually to find opportunities to optimize. But if you want to take a much deeper, much more detailed look at your website, you need an SEO crawler. In our next guide, we'll go over using our Site Crawl tool to improve your SEO.