If you’re reading this you’re probably already aware that optimizing your site will lead to enhanced performance, greater visibility and increased traffic. But, how do you successfully develop and implement an SEO strategy without firstly knowing what needs optimizing? Simple. By conducting an SEO audit of course!
Luckily for you WooRank is an advanced SEO auditing tool that analyzes tones of on and off-page SEO element as well as technical SEO factors to give you an instant SEO score. If that wasn’t enough it also produces a handy marketing checklist that you can work through to resolve any issues.
So, what’s the point of this article? Well, as a handy accompaniment to an awesome tool, we’ll be going through each of the tool’s checkpoints to help explain what is being examined, how it can help improve your site and how you can fix any issues. Alternatively, you can use the following SEO checklist to perform you own manual audit.
The three areas assessed in an SEO audit are:
- Technical SEO – this, in a nutshell, is your website upon which all other SEO is built. A website without a solid foundation will not perform well – this is very much the starting point as it helps search engines find and index your site
- On-page SEO – Refers to the content, keywords, other technical on-page elements which helps search engines and user better understand what’s on your site
- Off-page SEO – Refers all the SEO taking place externally (but relating) to your site which help search engines to determine the level of trust, value and authorship of your site.
Part 1. TECHNICAL SEO
Crawling & Indexing
- Broken links – Broken links are bad for usability and can hurt a site’s reputation by sending users to non-existent pages.
- Use a tool like the check my links Chrome extension to scan all the pages on your site for any broken links.
- Resolve any broken links
- Set your prefered domain in [Google Search Console] (https://www.google.com/webmasters) to make sure that traffic is redirected to your prefered domain
- Submit your XML sitemap to Google and Bing
-
Make sure that your robots.txt file isn’t blocking searching engines from crawling your entire site. To allow all search engines to crawl your entire site, your robots.txt file should look this:

- Submit and test your robots.txt file in Google Search Consol
- Use a tool like Screaming Frog to compile a list of all your URLs and check that they all use hyphens, and ideally contain the primary keyword for each corresponding page
- Remove any flash content, frames or iframes
- Use the NoFrames tag when you can’t avoid using frames
- Register your domain for a longer period of time. This demonstrates that your site is sticking around and provides a level of trust – always a good ranking signal
- Check that it isn’t going to expire any time soon
- Establish a blog on your site and publish content regularly.
Mobile Friendliness
- Rendering – Check to see how your site renders on mobile devices and give careful consideration to the following checkpoints
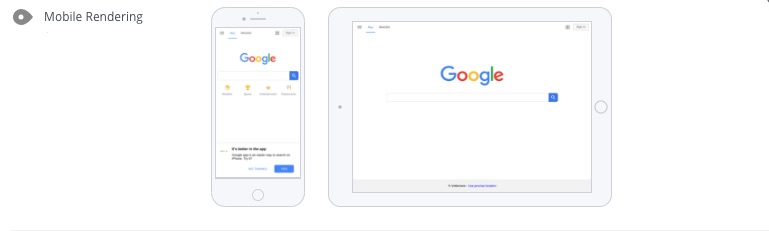
- Ensure that your website uses a responsive design – Search engines prefer this method, which ensures that content fits on all screen sizes without the need to have separate sites
- Touchscreen readiness – Does your design allow user to easily tap targets on a touch screen?
- Mobile compatibility – Check that your website does not embed any special types of web content such as Flash or java, which are not compatible with all mobile devices and browsers.
- Font size legibility – Check that your text is legible across all screen sizes. Check Google Typography guidelines for Android
2. Mobile viewport – This is an element of responsive design. The viewport tells browsers to render a page according to device screen width.
- Check that pages aren’t missing a meta viewport
- Check that content fits within the specified viewport size
3. Mobile speed – Speed is a vital mobile ranking factor and needs to be optimized. This means that ‘above the fold’ content must render in less than 1 second. You can improve this by addressing the following:
- Eliminate render blocking Javascript and CSS above the fold
- Prioritize visible content
- Leverage browser caching
- Optimize images (by reducing their size through compression)
- Avoid landing page redirects
Usability
- Favicon – Although this isn’t a ranking signal you should consider having a favicon for your site as it improves usability and brand recognition.
- Create a favicon and upload to site
- Check that you have a custom 404 page. Include a nice, apologetic message along with navigational links so that people can continue browsing your site.
- Simplify page templates: Remove any unnecessary plugins, tracking codes, advertisements and widgets.
- Minimize image sizes: Use an editor like Adobe Photoshop to save your images for the web devices. This reduces image file size while retaining image quality.
- Set browser’s cache: The browser cache stores website resources locally, on a computer. It remembers a site that you have visited and will be able to load it much quicker on subsequent visits. This can be changed accordingly to improve website speed.
- Ensure language has been specified.
- Make sure your site is optimized for multilingual sites.
- Develop a strategy to develop content that can be made into rich snippets and monitor success.
Technologies
- Server performance – Regular periods of downtime could result in a poor user experience. Excessive downtime can result in your site being removed from Google’s index.
- Monitor your server’s performance by using Uptime Notifications and contact your provider if you are having problems.
- Specify language/character encoding to prevent problems when rendering special characters.
- If you haven’t already, purchase a SSL certificate and migrate your site to HTTPS URLs (This isn’t necessarily a quick fix but it will be worth it in the long run).
- Check that all assets are hosted on new secure URLs
- Use a tool like Screaming Frog to compile a list of all URLs, or use Site Crawl to find all non-HTTPS assets such as images, CSS files, videos and scripts
Part 2. ON-PAGE SEO
HTML Improvements
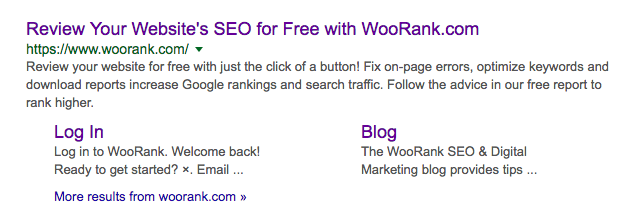
- Title Tags – This is the title that appears in browser tabs, bookmarks and search results. (see below) Use GSC HTML Improvements to highlight any issues.
- Check that each of your title tags are unique for every page.
- Check that they are between 50-60 characters long.
- Be sure to include your page’s primary keyword towards the beginning of the title.
- Write enticing descriptions with a strong call to action for every page.
- Include your primary search term, as this will be highlighted in bold in the SER.
-
Keep descriptions between 150-160 characters.
- Make sure that there is only one h1 title per page (unless you’re using HTML5).
- H1 titles should be unique and include the page’s primary keyword.
- You can use h2-h6 headers more frequently throughout.
- Check that images have alt attributes
- Keep the descriptions below 150 characters so that you don’t impact on page load speed
Keywords
- Page content – This could do with a post of it’s own, but ensure that you are using keywords properly and consistently on each page. Conduct proper keyword research and…
- Develop a keyword strategy.
- Implement your keywords in the correct manner.
- Measure success using the Keyword Tool (Available to Pro and Premium subscribers).This is an brilliant tool that allows you to not only track what position you appear in SERPs for specific keywords, but allows you to monitor up to 3 competitors for the same keywords as well. Keyword performance data is including in your Weekly Email Digest, sent right to your inbox. So simple.
Part 3. OFF PAGE SEO
Backlinks
- Backlinks – Backlinks are links that point to your site from an external website. The number and quality of backlinks are one of the most important ranking signals as they indicate trust, authority and quality content. However, they are probably the most difficult to obtain without time and dedication.
- Use a tool like Monitor Backlinks to gain a decent overview of your site’s and your competitors’ backlinks. This is a great tool because it shows you which links have the ‘nofollow’ attribute, as well as the domain authority of the site linking to yours (this is important as it determines the amount of link juice passed to your site), and allows you to disavow harmful links.
- Develop a backlink strategy to improve the number and quality of backlinks.
- Research business directories that you could sign up to (just remember to ensure that they are well moderated and not spammy as poor quality backlinks can be very harmful).
- Continuously to monitor your backlinks to ensure quality.
- Establish a presence on social media sites that are appropriate to your target audience. Research the best places to find potential customers.
- Develop a social media strategy and discover how to take advantage of these platforms.
- Encourage others to share your page content by including social share buttons on your site.
- Automate and monitor your activity with the help of these free social media tools.
- Register with Google My Business. This is extremely important to allowing your business to be featured on Google Maps. It will also allow you to obtain reviews, add images, and include opening hours which all contribute to your knowledge graph/panel.
- Create content specific to your local, for example ‘How to find a plumber in Manchester’.
- Register your site with local directory listings.
Well Done For Making It To The End.
So, there you have it! Our ultimate SEO audit is a great resource for taking a systematic approach to your SEO assessments. However, if you don’t want to do a manual audit, why not try the WooRank tool for a free audit. It will assess all of the above elements in seconds and provide you with further information about performance, site statistics and it has a new site crawl feature, eliminating the need to go from tool to tool.
Although doing any sort SEO audit can feel like a daunting task that will undoubtedly highlight some larger, long-term jobs, getting to grips with SEO now will ultimately pay off in the long run. Optimize your site and you’ll soon notice an improvement in pagerank, overall visibility and a healthy increase in site traffic. Good luck!