Conducting an SEO audit is simple, especially with great tools WooRank.
Simply type the URL of the website you wish to audit for an instant (and free!) overview of what is working well and what elements need some attention.
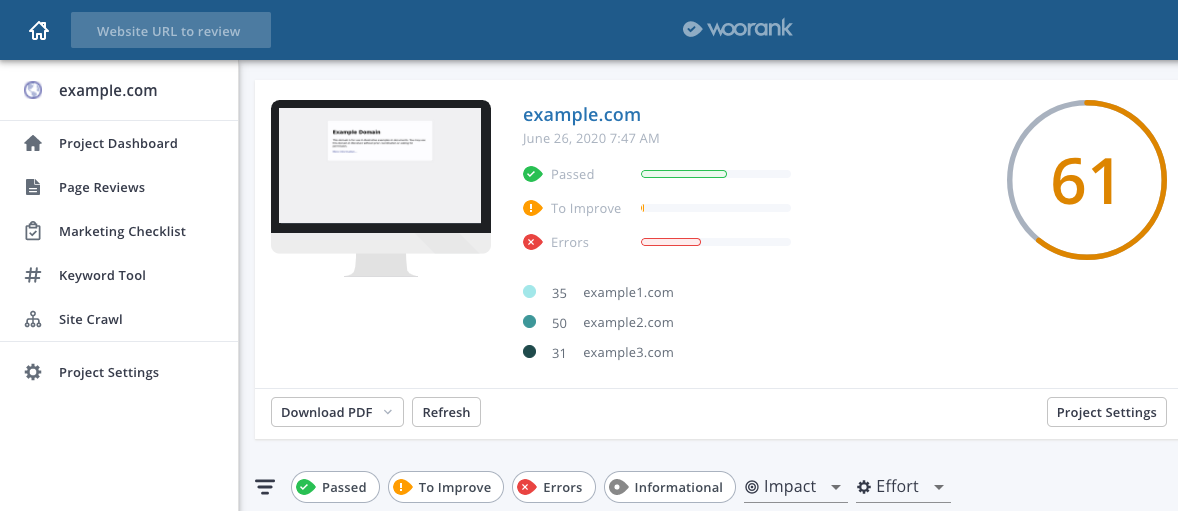
WooRank is one of the easiest auditing tools to use. It uses a visual traffic light system which allows you to see which elements have passed, which need improvement and which are being flagged as errors. Based on what the audit flags up, the overall SEO performance of your site is recorded as a number out of 100.
Generally, 70 is regarded as being pretty good - with a chance of ranking highly.
So what does the audit look at?
WooRank uses the following categories:
1. Optimize
This section includes a range of on-page and technical SEO elements that should be optimized, bucketed into different sections:
SEO
Title tags: It should be between 60-70 characters (to avoid being truncated in SERPs) and contain the keyword for the page to give search engines and users a better idea of the content on the page.
Meta Description: Although they don’t directly influence your SEO score, descriptions should be optimized and contain your keywords again to ensure that users know what they can expect to find, should they visit your page. Optimizing these can also increase the page’s CTR and lower bounce rate, two things that are ranking factors.
Headings: These are your <h1> tags. What WooRank is looking for here is that you’ve only used one <h1> tag on the page with <h2>-<h5> tags underneath. Not only does this help the user navigate and digest your page but h1-6 are read by search engines to decipher the content. So, make sure they contain your most important keywords.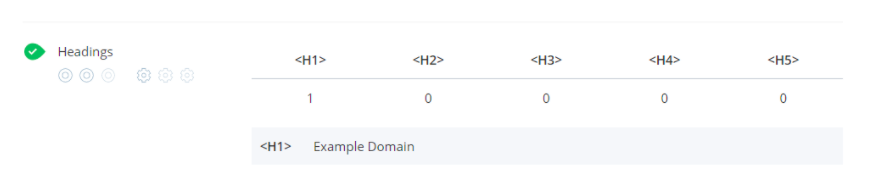
Keyword Consistency: Examines keyword usage across the most important places — title, description and headers. Use keywords inconsistently and you might struggle to rank.
Alt Attribute: It’s not a complete disaster for your site if your images are missing alt text, but it’s a missed opportunity to use keywords as well as rank in image search results. Make sure your images contain your page’s most important keyword and accurately describe the content of the image.
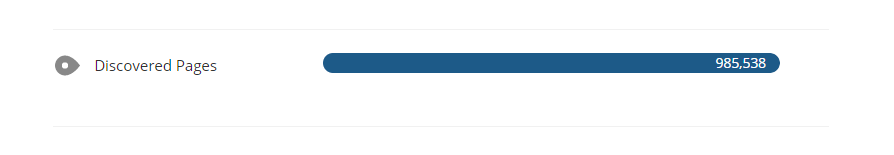
Discovered pages: Not a ranking signal but this is very handy for checking that your site’s pages are being indexed. If the number shown here doesn’t sound right you an in-depth Site Crawl technical analysis to find out why (we’ll come onto this a little later).
In-page Links: Because links will pass page authority, it’s a good idea to have high performing pages linking back to your homepage and vice versa. This will maximize the spread of link juice throughout your site.
Broken links: Broken links are bad for the user experience and your reputation which is precisely why Google doesn’t like them. If you have any broken links they’ll be displayed in an audit. Alternatively, you could use a tool like Check My Links to check the links across each of your pages.
WWW resolve: If you haven’t specified a preferred domain, i.e. with or without the www. prefix and you don’t redirect traffic from one URL to the other, search engines recognise both versions as two separate sites. This is bad news for your site because link juice will be shared between the two sites and Google will penalize sites with duplicate content. For some further reading on duplicate content, see our blog post about the most important technical SEO issues.
Robots.txt and sitemap:

If your site’s missing either of these it could be a reason for that low discovered pages count from before. Both of these are important for crawling and indexing and both should be submitted to the relevant search engine webmaster tools.
Underscores in the URL: Search Engines don’t recognize underscores (_) in URLs and won’t, therefore, regard them as being a space. If you create a URL like this example.com/Awesome_page_you_must_read, search engines will read it as example.com/Awesomepageyoumustread. It doesn’t sound like a huge deal at first, but it means your page looks less relevant to a keyword than example.com/Awesome-page-you-must-read.
Blocking Factors: Using Flash or Frames on your site may look nice but search engines can’t always crawl or index them. Avoid Flash when possible (try HTML5 instead), and use a NoFrames tag if you need to use a frame or iframe.
Mobile
Optimizing your site for mobile users is vital. Not only does Google give a boost to sites with a good mobile experience, mobile usage far surpasses desktop use. It’s important your site works well across all devices.
Mobile Friendliness: Mobile friendly pages make it really easy for users to complete an objective on a mobile device. Pages that don’t require the user to pinch and zoom or scroll side to side to find content and can easily push buttons are regarded as being friendly.
With WooRank, you can even see how your pages render across devices.
Touchscreen readiness: Assesses whether the most important information, like buttons and call to actions (CTAs), are big enough to be tapped easily.
Mobile Viewpoint: Checks to see if a mobile viewpoint has been configured and that the content fits within the viewpoint.
Mobile Speed: Since many users will abandon pages that take more than 4 seconds to load, it’s crucial that your mobile site is quick! WooRank evaluates
- Compression
- Caching
- Images optimization
- Landing page redirects
Usability
Remember that a good portion of SEO is about good user experience. Create an amazing online experience for your users and you’ll see results in rank position. Aspects of usability include:
Favicon: Although favicons aren’t an essential ranking signal they still help to create a better user experience. They create a unified brand experience and, if you get creative, can be fun for the user.
404 page: Not having a custom 404 page is bad for users and bots. They may struggle to understand where they’ve landed. Plus, generic 404 pages don’t have links to other pages on your site, so people will just leave the page, frustrated and angry with you.
Asset compression: Asset compression is a great way of optimizing page load speed. See our guide on increasing page load speed for more information on asset compression.
Asset cacheability: Caching assets like images and javascript files allows a browser to store these files locally so that it doesn’t have to download them every time the page is requested. Levering caching will reduce bandwidth and improve overall speed.
Structured Data Markup: This is used to create rich snippets that are handy for making your site distinctive from your competitors.
Technologies
WooRank will evaluate the technologies used on your site and will also show important information about your server and up-time. The most important things in this section are:
Page speed: If we’ve said it once, we’ve said it a thousand times: site speed is one of the most important factors in user experience and SEO. When auditing your site, check for different technical issues that will slow download time.
SSL security: In 2014 Google announced that URLs using HTTPS would get a ranking boost because of the trust that it instills in the user. It’s worthwhile to buy an SSL certificate and switching your site to HTTPS. Make sure you redirect traffic to HTTPS by implementing server-side 301 redirects.
2. Promote
Arguably the most important section here is the backlink counter. Use this to see how many backlinks your site has and how many referring domains. You’ll even be able to assess the quality of the referring domains. If you see a lot of poor quality referring domains use a tool like Monitor Backlinks to disavow them.
Social: WooRank assess your engagement across social media platforms. Instead of looking at likes or followers as measures how many times your site has been shared across social media.
If this isn’t as good as you’d expect, or you don’t get any website traffic from your Facebook page, it might be worth devising a social media strategy.
3. Measure
This section gives you an idea of the estimated traffic compared with other, similar or competing sites. It’s likely that this will increase if you get your SEO ship shape.
However, the real power of the Measure section is apparent when you upgrade your audit to a Project and sync your Google Search Console and Google Analytics accounts. This will bring in data for:
- Website visitors
- User behavior metrics like bounce rate and time on site
- Top search queries
- Crawl errors
Keyword Tool: Track keywords against your competitors’ keywords and overall performance. You can even use it to uncover the average monthly search volume for a specific search term to inform your research.
Site Crawl: This is an in-depth crawl of your site and uncovers on-page, content and technical errors that may be hindering your site’s ability to get indexed. It can detect missing or duplicate content, assets with HTTP or https status, canonical issues, and identify pages missing from your sitemap.
Special SEO Audits
An SEO audit like the one outlined here will work for any site, no matter what it's for. However, there are some tweaks, adjustments, and priorities that must be shifted to meet the specific needs of a website.
Learn what you should look out for when auditing your eCommerce site here.